Which Aluminum Profile T4, T5, T6 Is Better For Door & Window
Updated: 6 Jan 2025
Aluminum is often chosen as a material for extrusion because of its excellent mechanical properties. Aluminum's high ductility allows it to be easily processed into a variety of cross-sectional shapes. It consumes less energy during the forming process. In addition, the melting point of aluminum is about half that of ordinary steel, which makes the energy consumption of extruded aluminum profiles relatively low, effectively reducing tooling and manufacturing costs. Finally, aluminum has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal material for industrial applications.
During the extrusion process, subtle and almost invisible lines sometimes appear on the surface of the profile, which are caused by auxiliary tools during extrusion. To eliminate these marks, additional surface treatment methods can be selected. Secondary surface treatment operations such as end milling are often used to improve the surface finish of the profile section. These processing steps improve the overall profile of the part by reducing the surface roughness of the profile and optimizing the surface geometry. This type of treatment is usually used in application scenarios where high positioning accuracy of the parts is required or tight control of the mating surfaces is needed.
In the material description, common identifications such as 6063-T5/T6 or 6061-T4, among which "6063" or "6061" represents the grade of aluminum profile. At the same time, "T4", "T5," and "T6" indicate the processing state of the aluminum profile. So what are the differences between them?
For example, the 6061 aluminum profile performs better in strength and cutting performance and has higher toughness, good weldability, and excellent corrosion resistance. The 6063 aluminum profile has better plasticity and can achieve higher processing accuracy. At the same time, 6063 also has higher tensile strength and yield strength, shows excellent fracture toughness, and has high strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance.
T4 state refers to natural aging after solution treatment. That is, the aluminum profile is cooled after coming out of the extruder, but no artificial aging treatment is performed. The aluminum profile in this state has lower hardness and better plasticity, which is suitable for subsequent deformation processing, such as bending.
The T5 state is incomplete artificial aging after solution treatment; the aluminum profile is air-cooled and quenched and enters the aging furnace to keep the temperature at about 200°C for 2-3 hours. The aluminum profile in this state has a higher hardness and a specific deformation ability, which is the most commonly used state in curtain wall projects.
The T6 state is complete artificial aging after solution treatment. The aluminum profile is water-cooled and quenched after extrusion and then artificially aged for a longer time at a higher temperature to achieve a higher hardness, which is suitable for applications with higher hardness requirements.
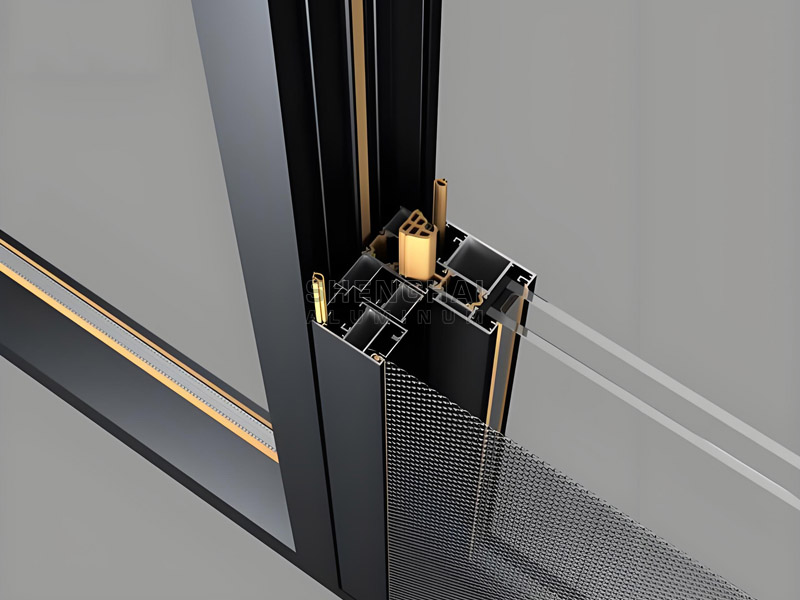 Mechanical properties of profiles
Mechanical properties of profiles
Yield strength: refers to the stress limit when a metal material begins to yield, that is, its ability to resist trace plastic deformation. For metal materials with no obvious yield point, the stress value that produces 0.2% residual deformation is usually used as the yield limit, called the conditional yield strength. When the external force exceeds this limit, the part will be permanently deformed and cannot be recovered.
Tensile strength: When the aluminum material yields to a certain extent, the internal grains are rearranged, and the ability to resist deformation is enhanced. Although the deformation intensifies at this time, it continues to change as the stress increases until the stress reaches a maximum value. After that, the material's ability to resist deformation is significantly reduced, and severe plastic deformation occurs at the weakest point, causing necking until fracture.
Webster hardness: The basic principle of Webster hardness is to press a quenching indenter into the material surface under the action of a standard spring. When the indentation depth is 0.01mm, it is defined as a Webster hardness unit. The hardness of the material is inversely proportional to the depth of indentation. The shallower the indentation, the higher the hardness, and vice versa.
Plastic deformation: Plastic deformation is a deformation that cannot be recovered by itself. When the force of a material or component exceeds the elastic deformation range, permanent deformation will occur; that is, there is still irrecoverable deformation after unloading, which is called residual deformation, which is plastic deformation.
 Aluminum is widely used in extrusion molding for its excellent properties, low production costs, and strong strength-to-weight ratio. Treatments like end milling can improve extrusion surface lines. Different processing states, such as 6061 and 6063, affect performance—6061 offers higher strength and processing ability, while 6063 provides better plasticity and toughness, catering to various engineering needs.
Aluminum is widely used in extrusion molding for its excellent properties, low production costs, and strong strength-to-weight ratio. Treatments like end milling can improve extrusion surface lines. Different processing states, such as 6061 and 6063, affect performance—6061 offers higher strength and processing ability, while 6063 provides better plasticity and toughness, catering to various engineering needs.
During the extrusion process, subtle and almost invisible lines sometimes appear on the surface of the profile, which are caused by auxiliary tools during extrusion. To eliminate these marks, additional surface treatment methods can be selected. Secondary surface treatment operations such as end milling are often used to improve the surface finish of the profile section. These processing steps improve the overall profile of the part by reducing the surface roughness of the profile and optimizing the surface geometry. This type of treatment is usually used in application scenarios where high positioning accuracy of the parts is required or tight control of the mating surfaces is needed.
In the material description, common identifications such as 6063-T5/T6 or 6061-T4, among which "6063" or "6061" represents the grade of aluminum profile. At the same time, "T4", "T5," and "T6" indicate the processing state of the aluminum profile. So what are the differences between them?
For example, the 6061 aluminum profile performs better in strength and cutting performance and has higher toughness, good weldability, and excellent corrosion resistance. The 6063 aluminum profile has better plasticity and can achieve higher processing accuracy. At the same time, 6063 also has higher tensile strength and yield strength, shows excellent fracture toughness, and has high strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance.
T4 state refers to natural aging after solution treatment. That is, the aluminum profile is cooled after coming out of the extruder, but no artificial aging treatment is performed. The aluminum profile in this state has lower hardness and better plasticity, which is suitable for subsequent deformation processing, such as bending.
The T5 state is incomplete artificial aging after solution treatment; the aluminum profile is air-cooled and quenched and enters the aging furnace to keep the temperature at about 200°C for 2-3 hours. The aluminum profile in this state has a higher hardness and a specific deformation ability, which is the most commonly used state in curtain wall projects.
The T6 state is complete artificial aging after solution treatment. The aluminum profile is water-cooled and quenched after extrusion and then artificially aged for a longer time at a higher temperature to achieve a higher hardness, which is suitable for applications with higher hardness requirements.

Yield strength: refers to the stress limit when a metal material begins to yield, that is, its ability to resist trace plastic deformation. For metal materials with no obvious yield point, the stress value that produces 0.2% residual deformation is usually used as the yield limit, called the conditional yield strength. When the external force exceeds this limit, the part will be permanently deformed and cannot be recovered.
Tensile strength: When the aluminum material yields to a certain extent, the internal grains are rearranged, and the ability to resist deformation is enhanced. Although the deformation intensifies at this time, it continues to change as the stress increases until the stress reaches a maximum value. After that, the material's ability to resist deformation is significantly reduced, and severe plastic deformation occurs at the weakest point, causing necking until fracture.
Webster hardness: The basic principle of Webster hardness is to press a quenching indenter into the material surface under the action of a standard spring. When the indentation depth is 0.01mm, it is defined as a Webster hardness unit. The hardness of the material is inversely proportional to the depth of indentation. The shallower the indentation, the higher the hardness, and vice versa.
Plastic deformation: Plastic deformation is a deformation that cannot be recovered by itself. When the force of a material or component exceeds the elastic deformation range, permanent deformation will occur; that is, there is still irrecoverable deformation after unloading, which is called residual deformation, which is plastic deformation.